Surface area is a central geometric concept with many practical applications, such as estimating paint coverage, quantifying heat loss, and calculating material costs. Precise computation of surface area is therefore essential.
The Surface Area Calculator provides immediate, accurate surface-area calculations for a broad set of 3D geometries — including cubes, rectangular prisms, spheres, hemispheres, cylinders, cones, pyramids, prisms, ellipsoids, capsules, toroidal surfaces, and body surface area (BSA). Select a shape, input the dimensions and units, and obtain results instantly.
What Is Surface Area?
Surface area denotes the aggregate area of every outer face and curved surface bounding a three-dimensional body. It is reported in square units such as m², cm², or in².
In simple terms:
- Perimeter measures length around a shape (1D)
- Area measures flat surfaces (2D)
- Surface area measures the outer covering of solids (3D)
Surface area calculations are widely used in construction, manufacturing, packaging, medicine, and science.
Surface Area Formulas at a Glance
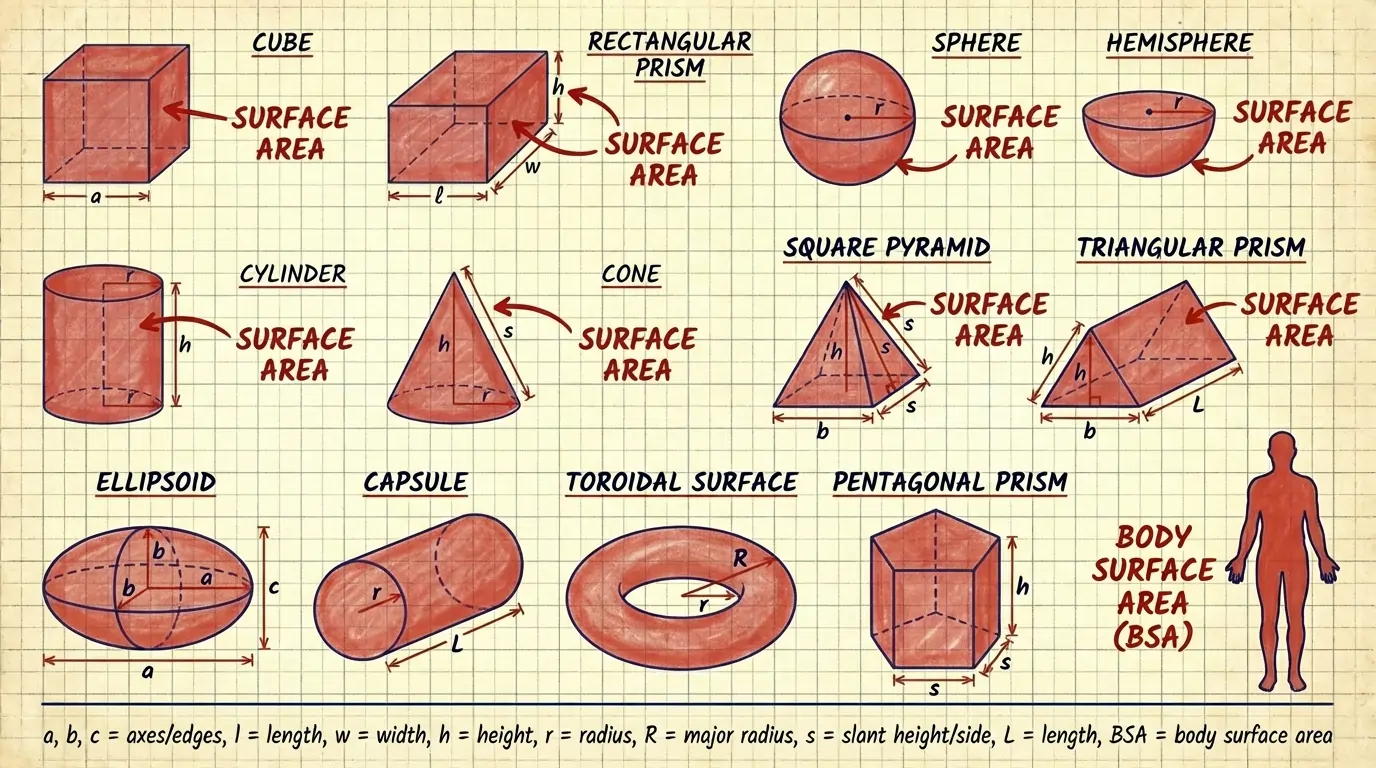
| Shape | Surface Area Formula |
|---|---|
| Cube | A = 6a2 |
| Rectangular Prism | A = 2(ab + bc + ac) |
| Sphere | A = 4πr2 |
| Hemisphere (closed) | A = 3πr2 |
| Cylinder (closed) | A = 2πr2 + 2πrh |
| Cone (closed) | A = πr2 + πr√(r2 + h2) |
| Square Pyramid | A = a2 + 2a√((a/2)2 + h2) |
| Triangular Prism | A = h(a+b+c) + 2Abase |
| Ellipsoid (approx.) | See detailed section below |
| Capsule | A = 4πr2 + 2πrh |
| Torus (Donut) | A = 4π2Rr |
| Body Surface Area | See BSA formulas below |
Where:
- a, b, c = side lengths
- r = radius
- R = major radius (torus)
- h = height
- Abase = area of base
How to Use the Surface Area Calculator
- Select a shape from the dropdown list
- Enter the required dimensions (radius, height, length, etc.)
- Choose your measurement unit (cm, m, in)
- Click Calculate to instantly get the surface area
The calculator automatically handles unit consistency and supports visual measurement guides for each shape.
Surface Area by Shape: Formula, Example, and Use Case
Cube:
Formula:
A = 6a2
Example:
a = 0.2 m
A = 6 × 0.22 = 0.24 m²
Use case:
Painting a cube-shaped storage box.
Rectangular Prism:
Formula:
A = 2(ab + bc + ac)
Example:
a = 2 m, b = 1 m, c = 0.5 m
A = 2(2 + 0.5 + 1) = 7 m²
Use case:
Packaging and shipping box materials.
Sphere:
Formula:
A = 4πr2
Example:
r = 0.3 m
A ≈ 1.13 m²
Use case:
Surface coating of spherical tanks or balls.
Hemisphere:
Formula:
A = 3πr2 (Closed Hemisphere)
Example:
r = 0.4 m
A ≈ 1.51 m²
Use case:
Domes and radar covers.
Cylinder:
Formula:
A = 2πr2 + 2πrh (Closed Cylinder)
Example:
r = 0.3 m, h = 1 m
A ≈ 2.45 m²
Use case:
Water tanks, pipes, columns.
Cone:
Formula:
A = πr2 + πr√(r2 + h2)
Example:
r = 0.2 m, h = 0.4 m
A ≈ 0.42 m²
Use case:
Funnels, cones, roofs.
Square Pyramid:
Formula:
A = a2 + 2a√((a/2)2 + h2)
Example:
a = 2 m, h = 1.5 m
A ≈ 10.77 m²
Use case:
Architectural structures.
Triangular Prism:
Formula:
A = h(a+b+c) + 2Abase
Base Area: Abase = ¼√{(a+b+c)(-a+b+c)(a-b+c)(a+b-c)}
Use case:
Structural beams and frameworks.
Ellipsoid:
Formula:
Approximate Formula:
A ≈ 4π[(apbp + apcp + bpcp)/3]1/p
Where p ≈ 1.6075
Use case:
Planetary modeling, medical imaging.
Capsule:
Formula:
A = 4πr2 + 2πrh
Example:
r = 0.5 m, h = 2 m
A ≈ 9.42 m²
Use case:
Pharmaceutical capsules, tanks.
Torus:
Formula:
A = 4π2Rr
Example:
R = 5 cm, r = 1 cm
A ≈ 197.39 cm²
Use case:
Seals, rings, industrial gaskets.
Body Surface Area (BSA):
Mosteller Formula:
BSA = √[height(cm) × weight(kg) / 3600]
Du Bois Formula:
BSA = 0.007184 × height(cm)0.725 × weight(kg)0.425
Use case:
Drug dosage calculation, burn assessment in medicine.
Units and Measurement Tips
- Always use consistent units
- Convert diameter to radius: r = d ÷ 2
- Torus: R = center-to-center distance, r = tube radius
- Ellipsoid axes should be measured carefully
- Avoid rounding until the final step
Frequently Asked Questions
Surface area is measured in square units such as m² or cm².
A = 4π2Rr.
No, it uses a close mathematical approximation.
Medical dosing, burn treatment, and physiological analysis.
No. Surface area measures outer coverage; volume measures space inside.
Final Thoughts
The Surface Area Calculator on Perimeter Calculator provides fast, accurate surface area calculations for both common and advanced 3D shapes. With correct formulas, unit handling, and visual guidance, it’s ideal for students, professionals, and everyday problem-solving.